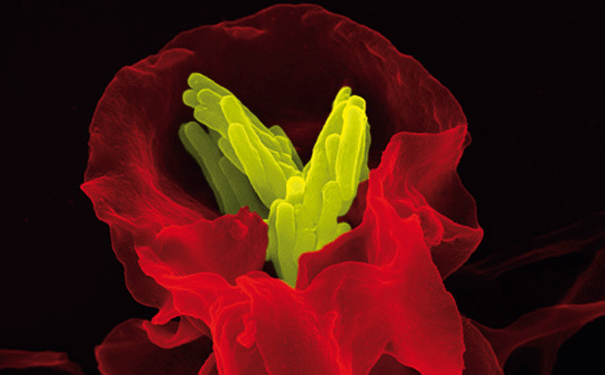
White blood cell destroying tuberculosis. Image: MPI for Infection Biology/Volker Brinkmann
Scanning electron microscope technology reveals the image of scavenger cell engulfing tuberculosis bacteria.
This coloured scanning electron microscope image shows a white blood cell [dyed red] in the process of destroying the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis [yellow]. The bacteria is surrounded by the cell membrane of a scavenger cell — a cell that engulfs and digests debris — then drawn inside and rendered harmless. Tuberculosis (TB) usually affects the lungs, and almost one third of the world’s population is infected with the disease. A healthy immune system can usually prevent the bacteria from activating. The bacteria can also be destroyed by ultraviolet rays in sunlight. Australia has one of the lowest incidence rates of TB in the world, for further information visit the Australian Medical Association.